The predecessor of light quantum theory is the quantum hypothesis proposed by Planck. Planck believes that radiation consists of a fraction of energy, just as a substance is composed of atoms. One part of energy in radiation is a quantum. The amount of energy depends on the wavelength of radiation, the shorter the wavelength, the greater the energy; the longer the wavelength, the smaller the energy. That is, the quantum energy is inversely proportional to the wavelength and is proportional to the frequency. Expressed by the formula: E = hν, where h is the Planck constant, v is the quantum frequency, and the relationship between quantum frequency and wavelength c = λf, f and v both represent the quantum frequency, but the symbols used are different. Subsequently, Einstein was influenced by the Planck Quantum Hypothesis and began to work on what was later called "light quantum theory." Einstein thinks that objects are made up of atoms one by one, discontinuous, and that light is continuous. Then why is there a photoelectric effect? In addition to continuity, can light have particle properties under certain conditions? With this kind of thinking, Einstein boldly assumed that light is just as particle-like as atoms, and that light is a stream of particles moving at a speed of c=3*108. These particles are named light quanta and the energy of light quanta is E. =hv. The theory of light quantum well explains the photoelectric effect. When a certain frequency of light hits the metal surface, if the frequency of this light reaches the limit frequency, no matter how long the light is irradiated, the metal surface will emit electrons. Using light quantum theory, this phenomenon can be well explained: Light is a particle with certain energy. These particles all have their own energy, which is proportional to the frequency of particles and inversely proportional to the wavelength. When light strikes the metal surface, the energy of the light particles is instantaneously transmitted. As long as the energy of the light quantum is large enough, electrons in the metal can overflow. Thus, the photoelectric effect is well explained. At the same time, according to the law of conservation of energy, the photoelectric effect equation is obtained: Rainfall Shower Head, Hand Held Shower Head, Stainless Steel Shower Head, Bathroom Shower Head ZHEJIANG KINGSIR VALVE CO., LTD. , https://www.kingsirvalve.com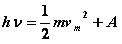 A is the electronic work function. The photoelectric effect is a good proof that light has particle properties, but some other phenomena of light, such as diffraction and interference of light, also indicate that light is fluctuating. So, in general, light has wave-particle duality.
A is the electronic work function. The photoelectric effect is a good proof that light has particle properties, but some other phenomena of light, such as diffraction and interference of light, also indicate that light is fluctuating. So, in general, light has wave-particle duality.