Pneumatic Cylinder Accessories Air cylinder accessories of different models and different standards are generally not interchanged. When ordering Pneumatic Cylinder accessories, please note the specifications and parameters of the corresponding cylinder. If the standard and model of the cylinder are same, the cylinder accessories can be used interchangeably.Pneumatic Cylinder Tube. Pneumatic cylinder is the executing component in pneumatic systems, mainly used to convert the pressure energy of compressed air into mechanical energy, generating linear or oscillatory motion. The construction of pneumatic cylinders is complex and includes multiple key components. Below are some common components and their functions: Cylinder Barrel: This is the main body of a cylinder, typically a cylindrical container used to accommodate pistons and other internal components. The cylinder barrel must be strong enough to withstand the pressure of compressed air inside. Piston: located inside the cylinder and in close contact with the inner wall of the cylinder barrel. When compressed air enters the cylinder, the piston moves inside the cylinder barrel, generating thrust or tension. Piston Rod: The part that connects the piston to the external mechanical structure and is used to transmit the linear motion of the piston. End caps/caps: fixed at both ends of the cylinder barrel, sealing the internal space of the cylinder and supporting the piston rod and other components. The front cover usually includes a guiding component for the piston rod. Seals: Used to prevent gas leakage and ensure smooth movement of the piston within the cylinder barrel. It mainly includes piston sealing rings, rod sealing rings, and dust sealing rings. Guide bushing: Helps the piston rod maintain the correct direction of movement, reducing friction and wear. Buffer Device: Some cylinders are equipped with buffer devices to slow down the speed of piston movement when it reaches the end point, preventing impact and noise. Magnetic switches: Some cylinders have built-in or external magnetic switches used to detect the position of the piston and control the action of the cylinder. Exhaust Flow Control Valve: Sometimes integrated into the cylinder, it is used to regulate the exhaust speed and control the speed of the piston. These components work together to enable the pneumatic cylinder to effectively convert the energy of compressed air into the required mechanical motion. According to specific application requirements, pneumatic cylinders may also include other specially designed components to meet specific functional requirements. Pneumatic Cylinder Accessories,Pneumatic Cylinder Parts Foshan Weiyingjia Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.wyspneumatic.com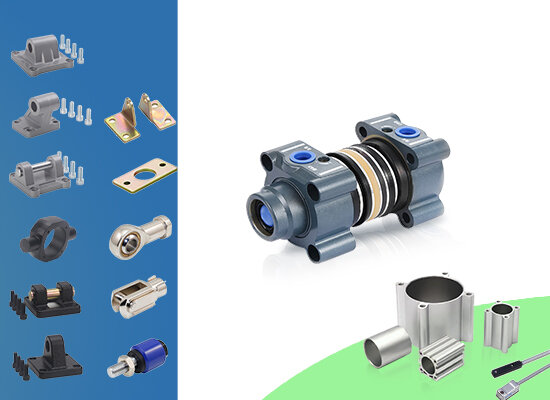
China's economy will focus on small-displacement cars in the next six years
From the end of 2005 to the start of 2006, China's economy is set for a new phase. The recently concluded Central Economic Work Conference outlined detailed plans for the country's economic development in the coming year. As 2006 marks the first year of the "Eleventh Five-Year Plan," it is crucial to understand the key policy directions and strategic priorities that will shape the nation’s economic trajectory.
**Watch Point 1: Economic Growth Will Not Pursue Excessive Speed**
The conference emphasized the importance of maintaining stable and sustainable growth, rather than chasing high-speed expansion. The government aims to ensure continuity in macroeconomic policies, avoiding sharp fluctuations that could destabilize the economy. This approach aligns with the broader goal of promoting quality growth, focusing on structural adjustments, efficiency improvements, and long-term stability. The "double-stable" fiscal and monetary policies remain unchanged, with continued efforts to manage investment and credit flows carefully to prevent overheating.
**Watch Point 2: Macro-control Will Target Overcapacity**
A major challenge for 2006 is addressing overcapacity in key industries such as steel, cement, and non-ferrous metals. The State Council has already warned that unchecked overinvestment could worsen industrial imbalances and hinder sustainable growth. With production capacities far exceeding demand, the government will intensify its efforts to eliminate outdated facilities and restrict new projects that do not meet environmental or efficiency standards. This will be a central focus of macro-control in the coming year.
**Watch Point 3: Consumption Will Be Expanded**
Expanding domestic demand remains a cornerstone of China's long-term economic strategy. While investment and exports have historically driven growth, consumption has lagged behind. To address this, the government will prioritize boosting household and rural consumption by improving living standards, expanding access to services, and creating a more favorable consumer environment. Tax cuts on housing and car purchases, along with relaxed restrictions on small vehicles, are among the expected measures to stimulate spending and drive internal demand.
**Watch Point 4: Investment Will Shift Toward Rural Infrastructure**
Rural areas remain a key challenge in China's development. The government has pledged to invest more in rural infrastructure and social programs to support the construction of a new socialist countryside. This shift from urban-focused investment to rural development is aimed at boosting local consumption, modernizing agriculture, and broadening domestic demand. It also represents a significant policy realignment that will have wide-reaching effects on economic growth.
**Watch Point 5: Oil Price Reform Will Be Prioritized**
Reforming energy pricing, particularly for oil and natural gas, is a top priority for the next year. This move is part of a broader effort to resolve deep-seated economic and social issues, including inefficiencies in resource allocation. Alongside this, state-owned enterprise reforms and financial sector restructuring will continue to be critical areas of focus. These changes aim to enhance competitiveness, improve governance, and prepare China's economy for deeper integration into the global market.
**Watch Point 6: Environmental Protection Will Be Embedded in Leadership Assessments**
Environmental protection is now being taken more seriously than ever. The conference highlighted the need to reduce energy consumption and pollution, especially in high-emission industries. A significant policy change involves incorporating environmental performance into the evaluation of local officials. This signals a stronger commitment to sustainability and long-term ecological health, ensuring that environmental concerns become a core part of decision-making at all levels of government.
As 2006 begins, these six watch points reflect the Chinese government's strategic vision for a more balanced, sustainable, and inclusive economic model. With a focus on stability, reform, and long-term development, the year ahead promises to be a pivotal one for China's economic future.
Pneumatic air cylinder accessories mainly include cylinder mounting brackets, piston rod connecting joints, repair sealing parts, magnetic reed switch, as well as cylinder assembly kits and cylinder barrels, piston rods etc.Air Cylinder Tube.